In the evolving landscape of industrial and enterprise wireless connectivity, few technologies have had the transformative impact of LoRaWAN. Short for Long Range Wide Area Network, LoRaWAN is a low-power, long-range wireless protocol specifically designed to connect battery-operated devices over unlicensed ISM spectrum. At AG Antenna, we recognize LoRaWAN’s critical role in enabling efficient, scalable communication for IoT and IIoT applications, especially in private network deployments where reliability, control, and extended range are non-negotiable.
What Is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN builds on LoRa, the physical layer modulation developed by Semtech that uses chirp spread spectrum (CSS) to achieve exceptional range and robustness. While LoRa handles the RF signal encoding, LoRaWAN serves as the MAC (Media Access Control) and network protocol, defining how devices communicate through gateways to centralized servers.
Managed by the LoRa Alliance, LoRaWAN is an open global standard that supports secure, bidirectional communication in a star topology, making it ideal for use cases that require scalable, low-bandwidth, and ultra-long-range communication without the cost or complexity of cellular networks.
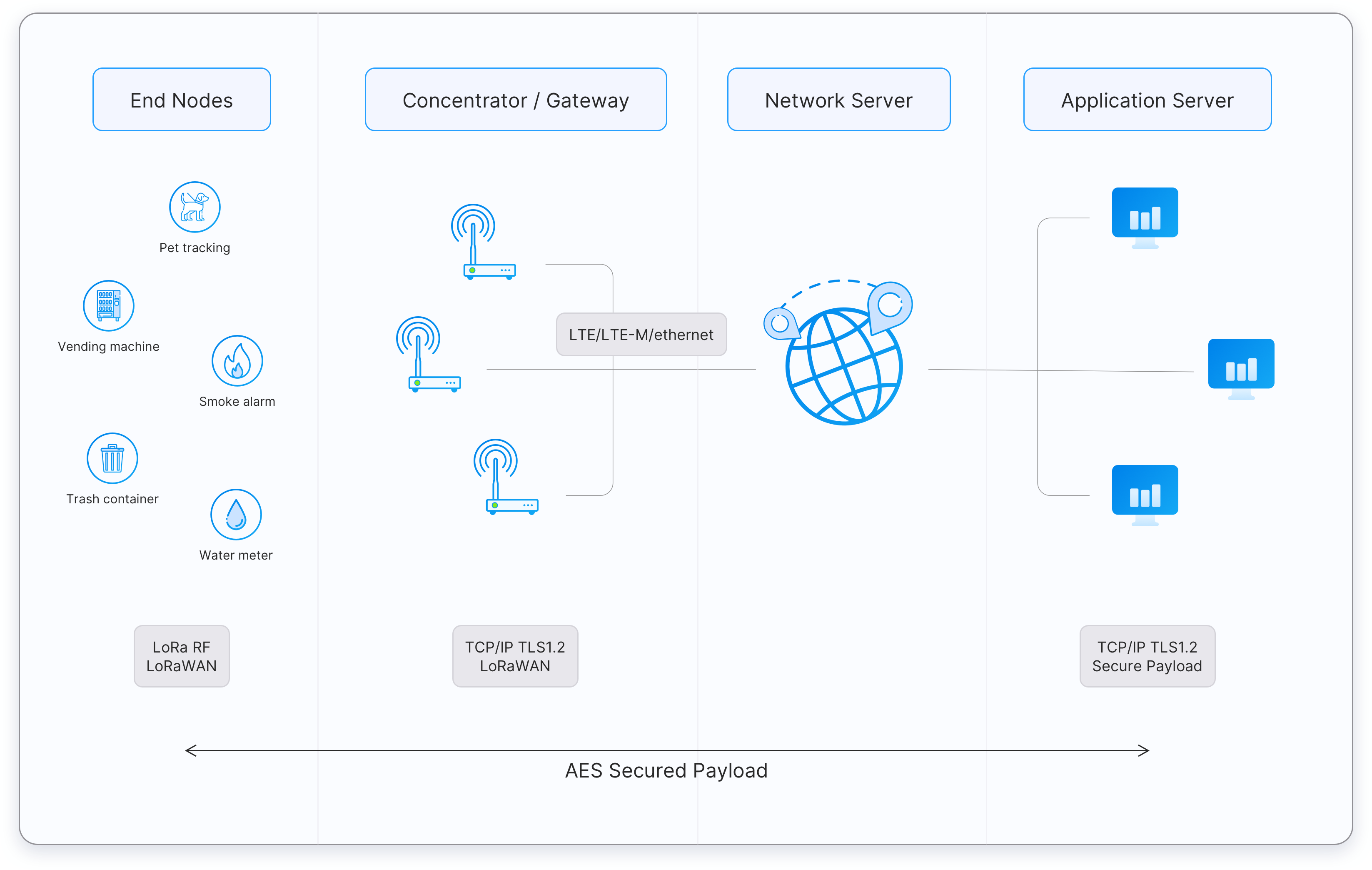
LoRaWAN Architecture and Device Classes
A typical LoRaWAN deployment consists of:
- End-devices (sensors or actuators)
- Gateways (bridging RF to IP)
- Network servers (managing packets, security, and routing)
- Application servers (where user data is processed)
End-devices are categorized into three classes:
- Class A: Ultra-low power, asynchronous transmission with receive windows triggered by uplink events.
- Class B: Adds scheduled downlink slots, synchronized via beacons.
- Class C: Always listening, designed for minimal latency and line-powered devices.
LoRaWAN also features Adaptive Data Rate (ADR), which dynamically adjusts spreading factors to balance range, energy consumption, and network capacity.
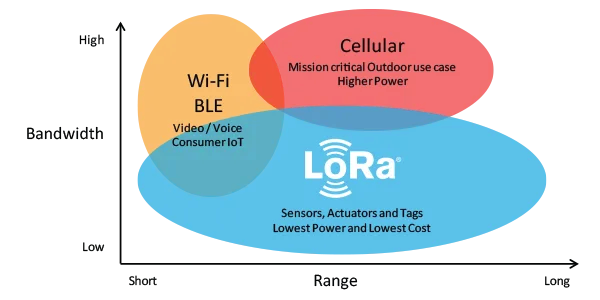
Why LoRaWAN Excels in Industrial Applications
LoRaWAN is purpose-built for scenarios where power efficiency, cost control, and long-range communication are paramount. Compared to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or even LTE-M/NB-IoT, LoRaWAN offers several unique advantages:
- Range: Up to 10 km in rural areas and several kilometers in urban environments.
- Battery Life: End-devices can operate for years without a recharge.
- Low Cost: Gateways and end-devices are inexpensive, with no carrier fees for private deployments.
- Scalability: A single gateway can support thousands of end-devices.
However, these benefits come with constraints: LoRaWAN is best suited for uplink-heavy, low-throughput applications with non-time-sensitive data. Duty cycle limitations (e.g., 1% in Europe) and downlink constraints must be accounted for in network planning.
LoRaWAN in the Real World: Common Use Cases
Smart Agriculture
From soil moisture probes to GPS-enabled livestock collars, LoRaWAN is revolutionizing precision agriculture. Sensors can transmit data from remote fields for years without battery replacement.
Smart Cities & Utilities
LoRaWAN enables smart lighting systems, parking sensors, and water meters that deliver real-time data over city-wide networks.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
LoRaWAN thrives in infrastructure monitoring, pipeline surveillance, and logistics. Predictive maintenance sensors using LoRaWAN can operate deep within facilities or across remote areas with minimal maintenance.
Asset Tracking & Cold Chain Monitoring
Track shipping containers, pallets, and temperature-sensitive goods across supply chains with LoRaWAN’s reliable coverage and low energy demands.
LoRaWAN’s Role in Private Networks
In enterprise and industrial environments, LoRaWAN’s value is amplified by private network architectures. By operating on unlicensed spectrum (902–928 MHz in North America), organizations gain complete control over their network infrastructure, without recurring fees or reliance on third-party carriers.
This autonomy is critical for:
- Utilities managing remote infrastructure
- Industrial campuses requiring on-site sensor networks
- Organizations deploying multi-network architectures that integrate LoRaWAN with LTE, Wi-Fi, or CBRS
AG Antenna Solutions for 815–928 MHz Private LoRaWAN Networks
At AG Antenna, we offer antenna systems engineered specifically for LoRaWAN networks operating in the 902–928 MHz ISM band. Our solutions are designed for rugged reliability, optimal gain, and precise tuning—delivering superior link budget performance in both rural and dense urban environments.
Key Products Include:
- MIMO XPOL and MIMO Low PIM Dual Slant directional antennas that enable LoRaWAN network leveraging with Anterix, CBRS, WiFi HaLow, WiFi 1/7 and LTE/5G spectrums. Ideal for routers engineered for extended reach, multi-band support.
- MIMO Omnidirectional 700MHz-6000Mhz Antennas Rugged outdoor LoRaWAN application antennas offering consistent wide area 360° coverage. Also ideal for deployment with multi-network gateways.
All AG Antenna LoRaWAN models are optimized for low VSWR, minimal PIM, and reliable performance in long-range industrial deployments. Our team works closely with integrators to ensure that antenna selection supports not just frequency compatibility—but the entire application environment.
Explore our lineup here: LoRaWAN 815 MHz Private Network Antenna Solutions
Bringing It All Together
LoRaWAN is redefining what’s possible in low-power, wide-area wireless networking, particularly for organizations demanding long-range, low-maintenance, and scalable solutions for IoT and IIoT. With the right antenna system, LoRaWAN deployments can achieve unparalleled performance, even in the most remote or RF-challenging conditions.
At AG Antenna, we deliver tuned, rugged, and deployment-ready antenna solutions that unlock the full potential of LoRaWAN networks. Whether you're building a private smart agriculture deployment or enabling industrial sensor grids, our antennas provide the reliable RF foundation you need.
Talk to our team today to find the ideal antenna for your LoRaWAN deployment.

